By Murray Wennerlund published 11-16-2024 updated 11-16-2024
|
|
|
By Supervisor published 4-29-2018 updated 3-21-2019

By Supervisor published 4-29-2018 updated 3-21-2019
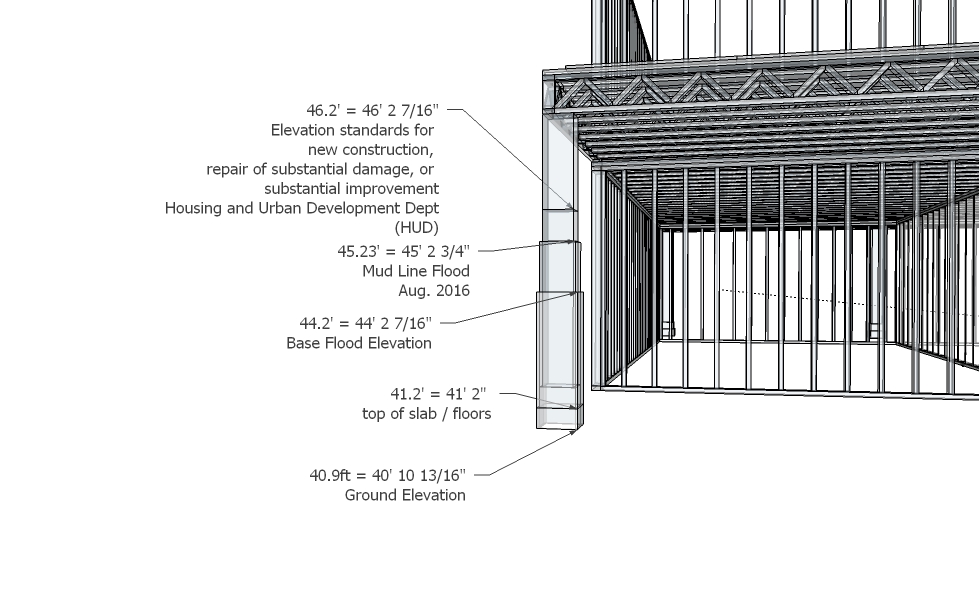
4. Elevation Standards
The elevation standards outlined below will apply to new construction, repair of substantial damage, or substantial improvement of structures located in an area delineated as a flood hazard area.
> All structures designed principally for residential use and located in the 1 percent annual (or 100- year) floodplain that receive assistance for new construction, repair of substantial damage, or substantial improvement must be elevated with the lowest floor, including the basement, at least two feet above the 1 percent annual floodplain elevation.
> Residential structures with no dwelling units and no residents below two feet above the 1 percent annual floodplain must be elevated or flood-proofed, in accordance with FEMA flood-proofing standards, to at least two feet above the 1 percent annual floodplain.
> All Critical Actions (defined as any activity for which even a slight chance of flooding would be too great because such flooding might result in loss of life, injury to persons, or damage to property) within the 0.2 percent annual floodplain (or 500-year) must be elevated or flood-proofed (in accordance with FEMA standards) to the higher of the 0.2 percent annual floodplain flood elevation or three feet above the 1 percent annual floodplain. If the 0.2 percent annual floodplain or elevation is unavailable for Critical Actions, and the structure is in the 1 percent annual floodplain, then the structure must be elevated or flood-proofed at least three feet above the 1 percent annual floodplain level.
Applicable state and local codes and standards for floodplain management that exceed these requirements, including elevation, setbacks, and cumulative substantial damage requirements, will be followed.